Weight Loss Surgery and Everything You Need to Know About It + Doctor’s Explanation

In the past, when people talked about losing weight, the only options were exercising and dieting. However, today, in addition to these two methods, weight loss surgery has become one of the most effective and healthy ways to lose weight.
This procedure is no longer seen as something strange or frightening. Over the past few years, it has become well-known and accepted among people who are overweight or obese.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | A set of surgical techniques that modify the digestive system to promote weight loss |
| Main Goals | Sustainable weight loss and improved metabolic health; treating obesity-related diseases; increasing life expectancy and quality of life |
| Types | Restrictive methods (e.g., Gastric Sleeve, Gastric Banding); Malabsorptive methods (e.g., Gastric Bypass); Combination methods (e.g., Mini Bypass, Duodenal Switch) |
| Ideal Candidates | BMI ≥ 40 or ≥ 35 with obesity-related conditions; unsuccessful non-surgical weight loss attempts; psychological readiness and commitment to lifestyle change |
| Expected Weight Loss | Around 60–100% of excess body weight |
| Surgery Duration | 30–60 minutes |
| Hospital Stay | 1–2 days on average |
| Recovery Period | Light activities after 1–2 weeks; heavy activities after 4–6 weeks |
| Approximate Cost (in Iran) | From 100 million tomans |
| Performed By | A bariatric and laparoscopic surgeon, preferably with certification from an obesity surgery association |
| General Benefits | Fast and steady weight loss; improvement or cure for type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea; higher self-confidence and quality of life |
| Risks | Surgical complications (bleeding, infection, thrombosis); vitamin and mineral deficiencies; possible weight regain if diet isn’t followed |
| Post-Surgery Care | Liquid and soft diet in the first weeks; vitamin and protein supplements; regular exercise and lifelong medical follow-up |
What Is Weight Loss Surgery and Why Is It Done?
Weight loss surgery, also known as bariatric surgery, refers to a group of surgical procedures that alter the stomach, intestines, or other parts of the digestive system to treat obesity.
These surgeries are performed under general anesthesia using laparoscopic (minimally invasive) techniques by a specialized bariatric surgeon.
How Does Bariatric Surgery Help With Weight Loss?
The main goal of weight loss surgery is to help treat obesity and related diseases. It allows patients to feel full sooner and lose excess weight gradually, in a healthy and sustainable way.
These methods have been approved by global medical organizations since 2002. They focus on two main mechanisms:
- Reducing stomach size, and/or
- Bypassing part of the digestive tract to limit food absorption.
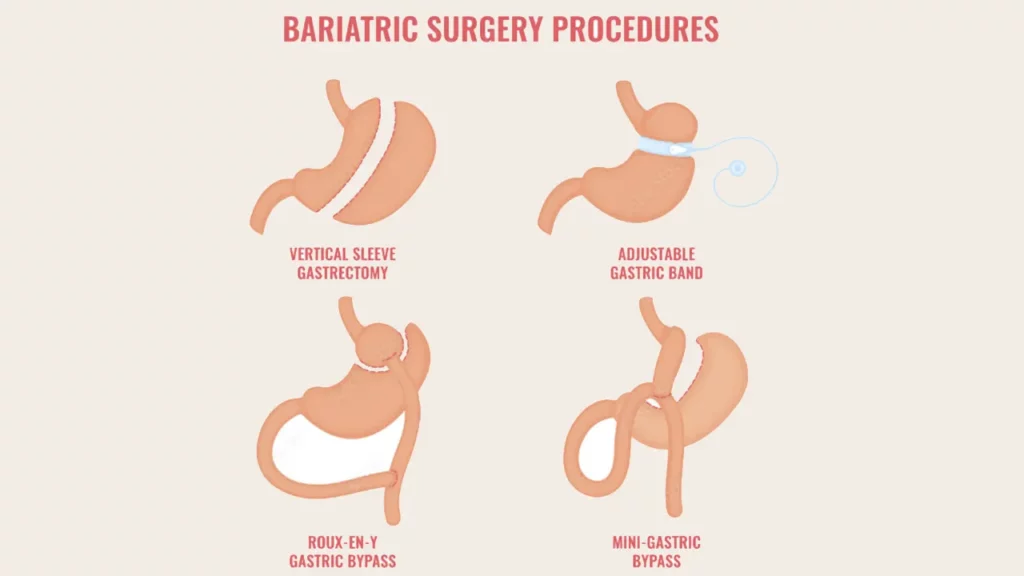
Types of Weight Loss Surgeries
Depending on the surgical approach, there are several main types of weight loss surgery:
- Restrictive procedures such as Gastric Sleeve or Gastric Plication reduce stomach capacity.
- Malabsorptive procedures such as Gastric Bypass or Intestinal Bypass reroute part of the digestive system, so less food is absorbed.
- Older methods like Gastric Balloon or Gastric Banding are now outdated and rarely performed.
Also read this: Can You Get a Gastric Sleeve After a Gastric Band?
Who Can Have Weight Loss Surgery?
To determine if you are a good candidate for weight loss surgery, you first need to calculate your Body Mass Index (BMI).
If your BMI is over 40, you are automatically considered eligible for the procedure.
If your BMI is over 35 and you also suffer from obesity-related conditions (like diabetes, fatty liver, hypertension, sleep apnea, or joint problems), you may also qualify.
Who Should Avoid Weight Loss Surgery?
This surgery is not recommended for everyone. It is suitable only for those who meet the medical criteria above.
For example, if you are only 10 kg (22 lbs) overweight, weight loss surgery is not appropriate. In such cases, a healthy diet, exercise, or medication are better options.
Is Weight Loss Surgery Done With Laser?
No. This is a surgical procedure, not a laser-based method. Laser fat reduction is a local, non-surgical technique.
Weight loss surgery is a laparoscopic (minimally invasive) operation performed by a qualified bariatric surgeon.
Step-by-Step Process of Weight Loss Surgery
Pre-Surgery Consultation and Tests
Before your operation, you will undergo a full medical evaluation. You must see specialists in cardiology, psychiatry, gastroenterology, pulmonology, and endocrinology.
You’ll also need to complete several tests such as blood work, urine tests, and abdominal ultrasound. In some cases, endoscopy may also be required.
Scheduling the Surgery
Once all results are ready, your surgery date will be scheduled. For international patients, test lists are provided remotely and reviewed by the surgeon before confirming the operation.
Hospital Admission
You’ll visit the clinic one day before surgery for a final checkup. Hospital admission can be done either the night before or the morning of the surgery.
Anesthesia and Surgery
You will be fully anesthetized before the operation. The procedure takes between 30 minutes to 1 hour, and all surgeries performed by Dr. Anbara are done laparoscopically.
This technique requires only a few small incisions and leaves minimal or no visible scars.
Recovery Room and Hospital Stay
After surgery, patients spend up to two hours in the recovery room under observation.
Most patients are discharged after one night in the hospital, though some may stay two or three nights depending on recovery speed.
Post-Surgery Diet and Instructions
For the first two weeks, patients must follow a clear liquid diet.
After that, they transition to soft foods, and by around two months post-surgery, most can eat normal meals again.
Also read this: Your Concerns About Sex After Weight Loss Surgery Are Completely Normal
Possible Risks and Complications
Like any surgery, weight loss surgery carries some potential risks — though these are rare when performed by an experienced surgeon.
Short-Term Risks
- Leakage from the stomach or surgical sutures
- Bleeding
Long-Term Risks
- Difficulty eating large portions for several months
- Vitamin or mineral deficiencies (requiring supplements)
However, with proper follow-up and adherence to medical advice, complications are minimal.
Benefits of Weight Loss Surgery
The advantages of weight loss surgery extend far beyond appearance:

- Significant and sustained weight loss
- Improved confidence and body image
- Better social and family relationships
- Enhanced physical activity and energy levels
- Reduced risk or remission of obesity-related diseases (e.g., diabetes, hypertension)
- Decreased need for medications.
Also read this: Benefits of Bariatric Surgery: How Weight Loss Surgery Transforms Lives
How Much Does Weight Loss Surgery Cost?
The cost of weight loss surgery varies depending on the country and hospital.
In Iran, prices typically start around 72 million tomans. For a full cost breakdown, you can refer to the detailed article on Weight Loss Surgery Costs.
Also read this: A Complete Guide to the Ideal Age for Weight Loss Surgery
FAQs About Weight Loss Surgery
When Is the Best Time to Have Weight Loss Surgery?
When your BMI reaches 40 or higher. If it’s above 35 with obesity-related health problems, you may also qualify.
How Much Weight Will I Lose After Surgery?
Depending on the type of procedure, patients typically lose 40–70% of their excess weight.
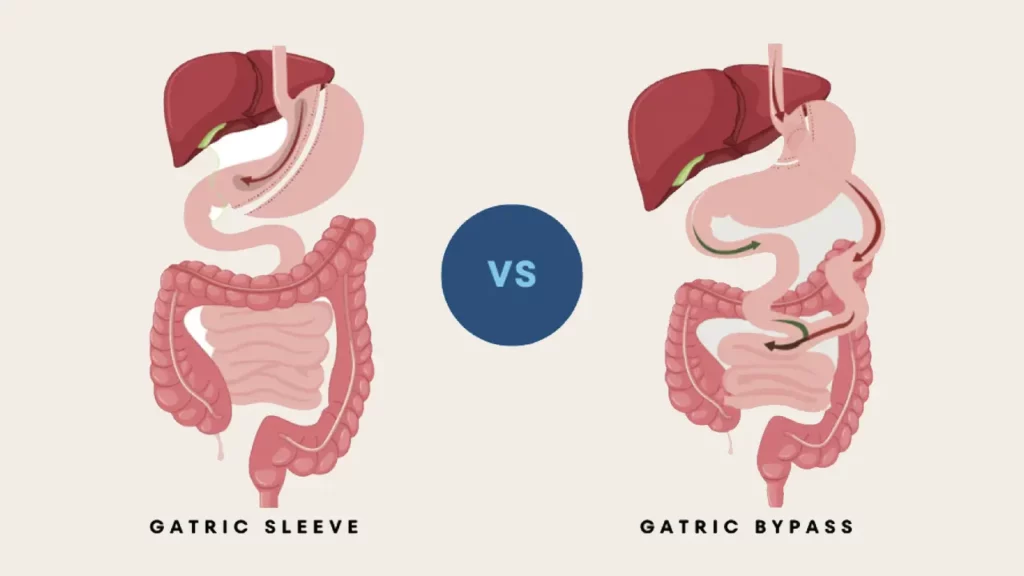
What Is the Difference Between Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass?
- Gastric Sleeve: Removes most of the stomach to reduce capacity.
- Gastric Bypass: Creates a small stomach pouch and connects it to the small intestine, bypassing most of the digestive tract.
FAQs About Weight Loss Surgery
If surgical standards and post-operative guidelines are followed properly, weight regain is very unlikely.
Among all types, gastric sleeve surgery is considered the safest and most effective.
Again, gastric sleeve surgery is the best long-term option, provided patients maintain a healthy lifestyle.
No. Lipomatic is a cosmetic, non-bariatric procedure and is not related to weight loss surgery methods like sleeve or bypass.