What Is Laparoscopic Surgery? (Everything You Need to Know About Laparoscopic Surgery)
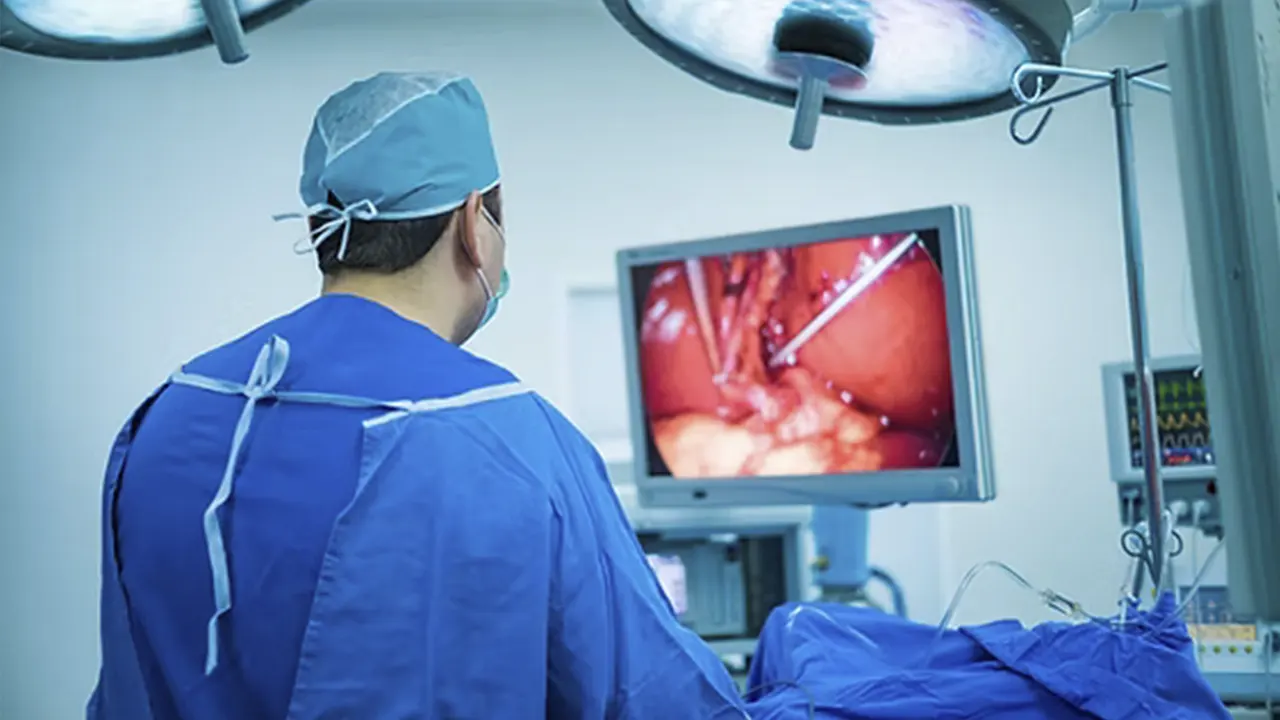
Laparoscopic surgery is a modern and advanced surgical technique used to perform operations in the abdominal and pelvic cavities. In this method, the surgeon inserts very thin and delicate instruments through tiny incisions made in the abdomen and pelvis. One of these instruments is the laparoscope, a special camera that transmits live images of the internal organs to a monitor. This allows the surgical team to observe the area and perform the entire operation with precision and control.
On this page, you will find comprehensive information about laparoscopic surgery, which is especially recommended for patients who are planning to undergo this type of procedure.
Laparoscopic Surgery at a Glance
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A modern surgical technique with very small incisions (2–4 cm) using a camera to view internal organs. |
| Comparison with Open Surgery | Laparoscopic surgery: small incisions, less pain, faster recovery. Laparotomy: large incision, more pain, longer recovery. |
| Common Uses | Weight loss surgeries (sleeve, bypass), gallbladder or appendix removal, hernia repair, gynecologic procedures (uterus, tubes), diagnostic surgeries. |
| Steps | 1. General anesthesia 2. Small incisions 3. CO₂ gas injected to inflate the abdomen 4. Insertion of camera and surgical tools 5. Performing surgery and closing incisions. |
| Advantages | Faster recovery, less pain, smaller scars, lower infection risk, shorter hospital stay. |
| Possible Complications | Infection, bleeding, injury to nearby organs, shoulder pain (caused by CO₂ gas), conversion to open surgery in rare cases. |
| Recovery | Discharge on the same or next day, return to light activity within 1–2 weeks, avoid driving for 24–48 hours. |
What Is the Difference Between Laparotomy and Laparoscopic Surgery?
In many situations, laparoscopic surgery can be used instead of a traditional laparotomy.
A laparotomy involves making a large incision in the abdomen to open the cavity completely. This conventional technique is still common but is more invasive and carries higher risks such as pain, infection, and longer recovery time.
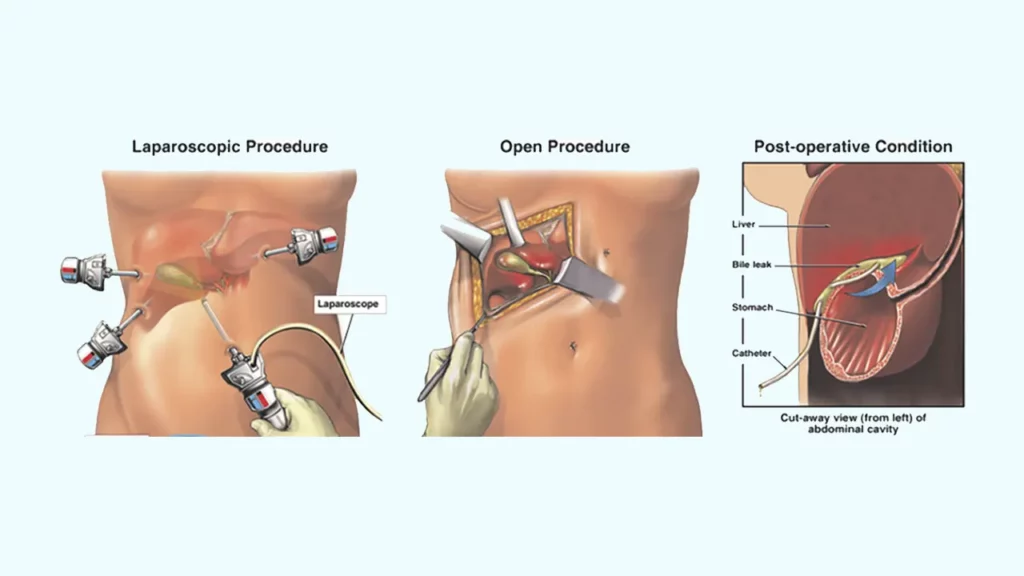
In contrast, laparoscopic surgery uses very small incisions, results in minimal complications, and offers a quicker and less stressful recovery. It also reduces overall costs and hospital stays, making it the preferred method for many types of surgery today.
When Is Laparoscopic Surgery Used?
The tools and techniques used in laparoscopic surgery are applied in a wide range of operations involving the abdomen, pelvis, joints, and more. Common procedures include:
- Removal of diseased organs such as the gallbladder or appendix
- Partial removal or repair of the stomach or colon
- Surgery on the urinary system, including the bladder, ureters, and kidneys
- Treatment of women’s reproductive organs, such as the uterus or fallopian tubes
- Tubal ligation
- Kidney donation from one person to another
- Weight loss surgeries like gastric sleeve and gastric bypass
- Hernia repair
- Examination of the liver or pancreas for cancerous tumors
- Exploratory surgery to identify unknown causes of abdominal symptoms
- Examination or removal of abdominal tumors
- Investigation of abdominal pain or scar tissue
- Locating internal bleeding or bruising when the patient’s blood pressure is stable
How to Prepare for Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery usually does not require extensive preparation compared to traditional surgery.
Patients typically attend one diagnostic consultation and undergo several preoperative tests to ensure they are ready for the procedure.

If you have any allergies, especially to anesthesia, bleeding disorders, or take blood-thinning medications such as aspirin or warfarin, you must inform your doctor beforehand.
Also, if you are pregnant, let your surgeon know, as this information helps the medical team plan your laparoscopic surgery safely and effectively.
How Is Laparoscopic Surgery Performed?
Laparoscopic surgery is considered a minimally invasive and relatively light procedure, often performed on an outpatient basis, meaning most patients can go home the same day if they feel well. It can be done in hospitals or specialized surgical clinics.
In most cases, the patient is placed under general anesthesia, though local anesthesia may be used for smaller procedures. The main steps of the surgery include:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Preparation | The surgeon makes 2–5 small incisions in the abdomen. |
| Creating Space | CO₂ gas is pumped into the abdominal cavity to inflate it, giving the surgeon a better view and space to operate. |
| Camera Insertion | A laparoscope (tiny camera) is inserted through one of the incisions, displaying live images on a monitor. |
| Performing Surgery | Guided by the monitor, the surgeon performs the operation using fine instruments inserted through other incisions. |
| Finishing Up | The gas is released, the instruments are removed, and the small incisions are closed with stitches or bandages. |
Expected Results After Laparoscopic Surgery
The outcome of laparoscopic surgery depends on the purpose and type of procedure performed.
In most cases, patients recover with minimal discomfort due to the small incisions. Results are often excellent, and patients experience much faster healing compared to open surgery.

However, if you experience any of the following symptoms after surgery, contact your doctor immediately:
- Headache or fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Bleeding, discharge, or redness at incision sites
- Swelling near the surgical area
- Difficulty urinating
- Persistent pain not relieved by prescribed medication
Recovery and Postoperative Care
It is normal to feel some pain or discomfort at the incision sites after laparoscopic surgery. Your doctor will prescribe painkillers to help manage this.
If stitches were used, they are usually removed within one or two weeks.
Sometimes, residual CO₂ gas can cause temporary shoulder pain. This happens because the same nerves that reach the shoulders also affect the diaphragm, which may be irritated by the gas. This discomfort usually disappears within a few days.
Gas pressure may also cause frequent urges to urinate, but this resolves naturally. Your doctor will tell you when it is safe to eat and drink again.
Most patients can return home once they are stable, but driving is not recommended immediately after discharge.
Risks and Complications of Laparoscopic Surgery
In the majority of cases, laparoscopic surgery is very safe and free from complications when performed by an experienced surgical team. However, as with any operation, minor risks may occur.
Possible complications include:
- Infection
- Internal bleeding if the procedure is not performed properly
- Small scars at incision sites
- Reaction to anesthesia
During laparoscopic surgery, the following rare risks may also occur:
- Accidental injury to a blood vessel or organ, leading to bleeding or damage
- Scar tissue from previous surgeries making it difficult to insert the trocar (a pointed instrument used in surgery)
- Obstruction of gas flow inside the abdomen due to internal adhesions
If complications occur, the surgeon may decide to switch from laparoscopic surgery to open surgery (laparotomy) for patient safety.
It is important to emphasize that when the operation is performed by a qualified and skilled surgeon, laparoscopic surgery is extremely safe and effective.
When Is Laparoscopic Surgery Not Recommended?
While laparoscopic surgery is generally safe, in some cases surgeons may choose not to use this method.
For example, if there is severe inflammation or swelling of the internal organs, or if the laparoscope does not provide a clear view, the surgeon may decide to perform a laparotomy instead.

Frequently Asked Questions About Laparoscopic Surgery
Pain is significantly less than with open surgery and is usually manageable with mild painkillers.
Only surgeons who have completed specialized training in laparoscopic techniques can perform it. These include general surgeons, gynecologists, orthopedic surgeons, and bariatric (weight loss) surgeons.
Yes, but they are very small (2–4 cm) and barely noticeable.
CO₂ gas is used to create space inside the abdomen, allowing the surgeon to see and operate more effectively.
Most patients can return to work about one week after laparoscopic surgery, though recovery time may vary depending on the type of operation.