What Is Gastric Bypass Surgery?

In Iran, the most common bariatric surgery is the sleeve gastrectomy, followed by gastric bypass surgery. While gastric bypass surgery is more popular in many other countries, it is not as widely performed in Iran. In this article, we will explain everything you need to know about gastric bypass surgery, including its mechanism, benefits, risks, and who is eligible for it. We will also compare sleeve surgery vs gastric bypass surgery to help you choose the right option.

Overview of Gastric Bypass Surgery at a Glance
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | One of the most effective bariatric surgeries that reduces stomach size and reroutes intestines to limit food intake and nutrient absorption. |
| How It Works | 1. Creation of a small stomach pouch (≈30 ml) 2. Connecting it directly to the small intestine (bypassing part of the stomach and intestine) |
| Ideal Candidates | BMI ≥ 40, or ≥ 35 with obesity-related diseases (diabetes, hypertension); motivated for lifestyle changes |
| Expected Weight Loss | 70–80% excess weight loss in 18–24 months; 60–80% improvement in obesity-related diseases (e.g., type 2 diabetes) |
| Surgery Time | 30–70 minutes (laparoscopic) |
| Hospital Stay | 1–2 days |
| Recovery Time | Return to light work: 1–2 weeks Full activity: 6–8 weeks |
| Cost in Iran | From 110 million tomans |
| Performed By | Experienced bariatric surgeon specializing in advanced laparoscopy |
| Advantages | Rapid, long-term weight loss; major improvement in type 2 diabetes; reduced appetite due to hormonal changes |
| Risks | Vitamin deficiencies (B12, iron, calcium); dumping syndrome; lifelong follow-up required |
| Post-Op Care | Step-by-step diet, daily supplements, regular exercise, follow-up lab tests |
Key Notes:
- Ideal for patients with severe acid reflux or a strong sweet craving.
- Weight regain is possible without proper lifestyle habits.
What Is Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Gastric bypass surgery is a minimally invasive laparoscopic procedure designed to help patients with severe obesity achieve significant and lasting weight loss. It is typically recommended for patients with a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or a BMI above 35 with obesity-related medical conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
How Does Gastric Bypass Surgery Work?
During gastric bypass surgery, the surgeon changes the normal digestive pathway from the esophagus to the intestines. A small pouch is created from the upper portion of the stomach, and the intestines are connected directly to this pouch.
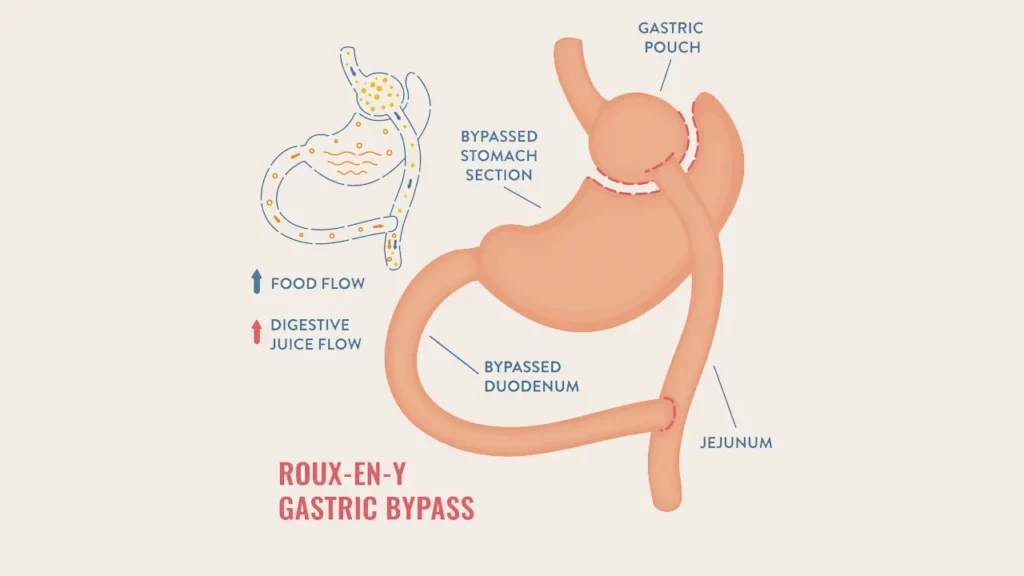
As a result:
- Food bypasses the majority of the stomach and part of the intestine.
- Patients feel full very quickly and eat less.
- Fewer calories and nutrients are absorbed.
This dual approach — restricting food intake and reducing absorption — is what makes gastric bypass surgery highly effective.
Who Can Have Gastric Bypass Surgery?
This surgery is not recommended for everyone. Candidates typically include:
- Individuals with BMI ≥ 40
- Individuals with BMI ≥ 35 and at least two obesity-related conditions (e.g., type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart disease)
- Patients who cannot achieve a healthy weight through diet and exercise alone
Benefits and Advantages of Gastric Bypass Surgery
- Long-term weight loss (60–80% of excess weight)
- Limits food intake
- May increase energy expenditure
- Improves gut hormones, reducing appetite and increasing satiety
- Very low weight-regain rate
- Reversible procedure
- Significantly improves type 2 diabetes and reduces medication dependence
- Helps treat obesity-related diseases such as hypertension and sleep apnea

Risks and Side Effects of Gastric Bypass Surgery
- Higher complication rate compared to sleeve gastrectomy
- Long-term risk of vitamin and mineral deficiencies (B12, iron, calcium, folate)
- Longer hospital stay than sleeve surgery
- Requires strict lifelong vitamin supplementation and dietary adherence
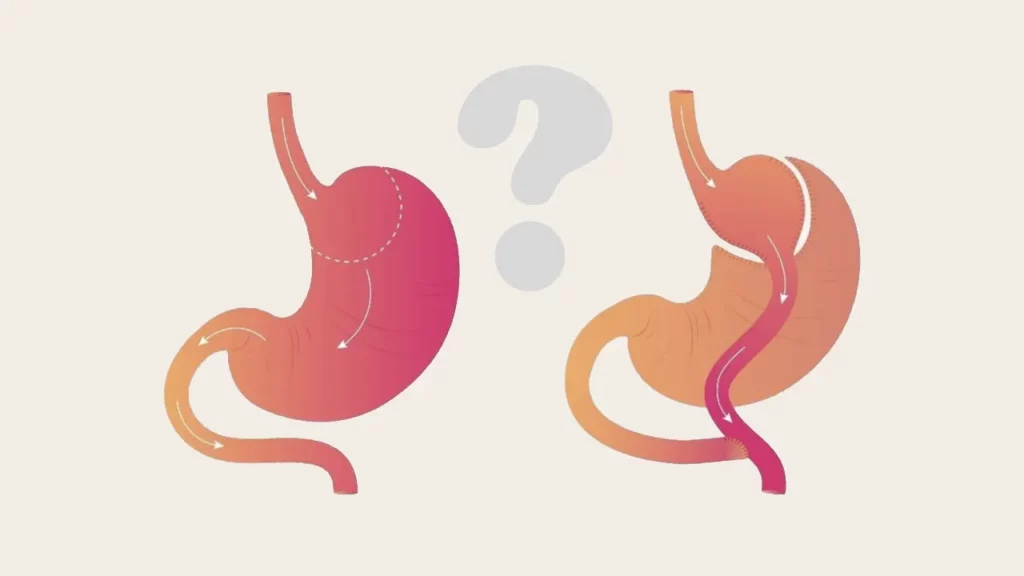
Sleeve vs Gastric Bypass Surgery: Which Is Better?
Sleeve gastrectomy is one of the safest and most popular bariatric procedures and is generally favored over gastric bypass surgery. However, each surgery has its own advantages.
Invasiveness
Both are laparoscopic. Sleeve is less invasive, as it removes part of the stomach without altering the intestines.
Gastric bypass surgery separates the stomach into two sections and reroutes the intestines, making it more complex.
Reversibility
- Sleeve gastrectomy: Not reversible
- Gastric bypass surgery: Reversible
Nutrient Absorption
- Sleeve: Food intake is reduced, but nutrient absorption remains mostly normal
- Gastric bypass surgery: Lower nutrient absorption → lifelong vitamin supplements required

Effectiveness on Obesity-Related Diseases
Both improve diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea, but gastric bypass surgery may be slightly more effective in severe cases.
Effectiveness for Severe Obesity
For patients with very high BMI, gastric bypass surgery may result in better weight loss.
For moderate obesity, sleeve may be a better choice.
Cost
Gastric bypass surgery typically costs more due to surgical complexity.
Also read this: Sleeve or Bypass: Comparing Advantages and Disadvantages
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, but gradually and with your doctor’s approval. Heavy exercise is usually safe after 3–6 months.
Yes, absorption of certain medications, including hormonal birth control and psychiatric medicines, may change. Consult your doctor for dose adjustments.
Yes, about 20–30% of patients may regain some weight after 5–10 years, usually due to lifestyle habits. Proper diet and exercise help prevent it.
Studies show patients may live 10–15 years longer on average — provided they follow medical and dietary recommendations.